Wood, a timeless and renewable resource, has played a crucial role in human history, providing shelter, tools, and aesthetic appeal. Understanding the process of how wood is made, its diverse uses, as well as its advantages and disadvantages, unveils the remarkable nature of this material.
Formation of wood
Wood originates from the vascular tissues of trees. Trees, primarily composed of cellulose, lignin, and hemicellulose, undergo a process known as photosynthesis. During this process, they absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, while sunlight converts into chemical energy. The energy is then used to synthesize glucose, which serves as the building block for cellulose—a key component of wood.Wood growth is marked by annual rings, forming as trees experience seasonal changes. These rings differ in size and density, providing a record of the tree’s growth history. This unique feature not only contributes to the aesthetic appeal of wood but also helps determine its strength and durability.
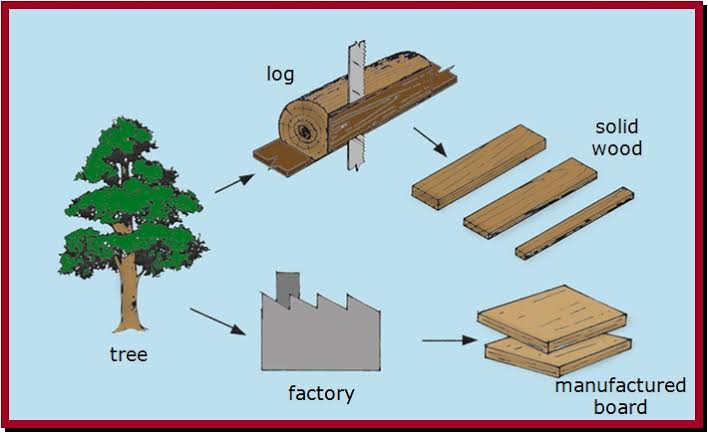
Uses of wood
Wood boasts an extensive range of applications, making it a versatile material. In construction, wood is used as a material for framing, flooring, and finishing. The furniture industry relies heavily on wood for crafting diverse pieces. Moreover, wood is a popular choice for artistic and decorative purposes, with its aesthetic appeal enhancing interior and exterior designs. Beyond aesthetics, wood is utilized in the production of paper, providing a sustainable alternative to synthetic materials. Additionally, wood plays a crucial role in the energy sector, serving as a renewable source for biomass fuel.

Advantages of wood
Renewability: Wood is a renewable resource, as trees can be replanted and harvested sustainably.
Versatility: Its versatility allows for a wide range of applications in construction, furniture, and art.
Aesthetic Appeal: The natural beauty of wood enhances the visual appeal of various products and architectural designs.
Carbon Sequestration: Trees absorb carbon dioxide during growth, acting as a natural carbon sink and contributing to environmental balance.

Disadvantages of wood
Vulnerability to Decay: Wood is susceptible to decay, especially when exposed to moisture and pests. Deforestation Impact: Uncontrolled logging can lead to deforestation, disrupting ecosystems and habitats.
Fire Hazard: While treated for fire resistance, wood remains combustible, posing a fire hazard.
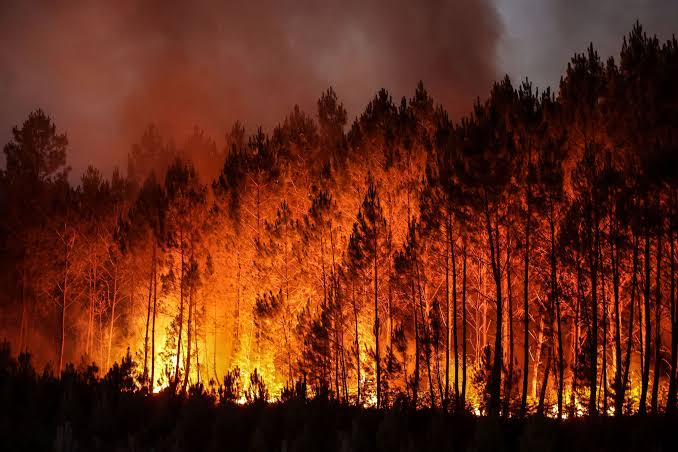

Wood stands as a testament to nature’s ingenuity, offering an array of benefits alongside challenges. Sustainable forestry practices and innovative technologies are essential to maximize the advantages of wood while mitigating its disadvantages, ensuring that this timeless material continues to enrich our lives.




