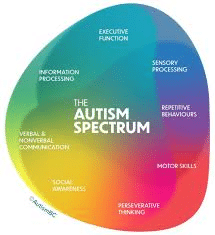
Autism, also known as Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), is a developmental disorder characterized by challenges with social interaction, communication, and repetitive behaviors. The term “spectrum” reflects the wide variation in challenges and strengths possessed by each person with autism. ASD includes conditions such as Asperger syndrome and childhood disintegrative disorder, previously considered separate.
Causes
The exact cause of autism remains unknown, but it is believed to be a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors:
- Genetic Factors: Numerous genes appear to be involved in autism. Some genetic mutations are inherited, while others occur spontaneously.
- Environmental Factors: Prenatal exposure to certain environmental agents such as valproic acid, thalidomide, or maternal infections has been associated with an increased risk of autism.
- Neurobiological Factors: Abnormal brain development and connectivity have been observed in individuals with autism, indicating that the disorder has a neurological basis.

Characteristics
Autism presents with a broad range of characteristics, which can be categorized into core symptoms and associated features:
- Core Symptoms:
- Social Communication Challenges: Difficulty with verbal and non-verbal communication, trouble understanding social cues, and challenges in developing, maintaining, and understanding relationships.
- Repetitive Behaviors: Engaging in repetitive actions or speech, strict adherence to routines, and intense interest in specific topics or activities.
- Associated Features:
- Sensory Sensitivities: Over- or under-reactivity to sensory inputs such as sounds, lights, textures, or smells.
- Cognitive Variability: While some individuals with autism have intellectual disabilities, others may have average or above-average intelligence, often excelling in specific areas such as mathematics, music, or art.
Risk Factors
Several risk factors have been identified that may increase the likelihood of developing autism:
- Family History: Families with one child with autism are at a higher risk of having another child with the disorder.
- Gender: Boys are about four times more likely to be diagnosed with autism than girls.
- Parental Age: Advanced parental age at the time of conception has been linked to a higher risk of autism.
- Other Medical Conditions: Certain genetic or chromosomal conditions, such as Fragile X syndrome or tuberous sclerosis, are associated with a higher incidence of autism.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing autism involves a combination of developmental screening and comprehensive diagnostic evaluation:
- Developmental Screening: Regular screenings during well-child checkups can help identify early signs of autism. Tools such as the Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (M-CHAT) are commonly used.
2.Diagnostic Evaluation: A thorough assessment by a team of specialists, including a developmental pediatrician, psychologist, neurologist, and speech therapist, is essential. This evaluation includes observing the child’s behavior, interviewing parents, and using standardized diagnostic tools like the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS) and the Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised (ADI-R)
Treatment
While there is no cure for autism, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life:
- Behavioral Therapies: Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) is a widely used approach that focuses on improving specific behaviors and skills. Other therapies include Pivotal Response Treatment (PRT) and Early Start Denver Model (ESDM).
- Speech and Language Therapy: Helps improve communication skills.
- Occupational Therapy: Focuses on enhancing daily living skills and sensory integration.
- Medications: While no medications can cure autism, certain drugs can help manage symptoms such as anxiety, depression, or hyperactivity.
- Educational Interventions: Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) are tailored to meet the specific needs of children with autism in school settings.
Coping Strategies
Families and individuals with autism can adopt various strategies to cope with the challenges associated with the disorder:
- Support Groups: Joining support groups can provide families with emotional support and practical advice from others facing similar challenges.
- Routine and Structure: Establishing consistent routines can help individuals with autism feel more secure and reduce anxiety.
- Skill Development: Focusing on building strengths and skills can boost confidence and independence.
- Professional Support: Regular consultations with therapists and specialists can help address ongoing challenges and adapt strategies as needed.





