
Fear and anxiety are closely related emotional states but have distinct differences:
Fear
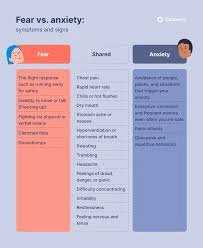
Fear is a response to a specific and immediate threat, whether real or perceived. It is typically characterized by a feeling of impending danger or harm, accompanied by physiological responses like increased heart rate, sweating, and a heightened sense of alertness. Fear often has a clear trigger, such as encountering a dangerous animal or being in a life-threatening situation.
Anxiety
Anxiety, on the other hand, is a more generalized feeling of unease, worry, or apprehension about something that may happen in the future. Unlike fear, which is usually linked to a specific threat, anxiety can arise from a variety of sources and may not always have a clear cause. People experiencing anxiety may feel tense, restless, or have difficulty concentrating, and their symptoms can persist over time, even in the absence of an immediate threat.
In summary, fear is a response to a present danger , while anxiety is a response to a perceived or anticipated threat that may or may not be immediate.
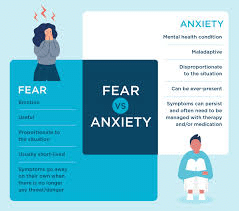
What is fear :Fear is an emotional response to a perceived threat, whether real or imagined. It triggers a cascade of physiological changes in the body, preparing it to either confront the threat (fight) or escape from it (flight). Fear is a fundamental survival mechanism that evolved to help humans and other animals respond to danger and protect themselves from harm. It can manifest as a range of sensations, including increased heart rate, sweating, trembling, and heightened alertness. Fear can be triggered by various stimuli, such as loud noises, sudden movements, or situations perceived as dangerous or threatening.
What is an anxiety :Anxiety is a psychological state characterized by feelings of worry , nervousness , or unease about something with an uncertain outcome. Unlike fear, which is usually a response to a specific threat, anxiety is often more generalized and can persist over time. People experiencing anxiety may have difficulty controlling their worries, may feel tense or restless, and may experience physical symptoms such as increased heart rate, sweating, and gastrointestinal discomfort . Anxiety can be triggered by various stressors, including work or school pressures, relationship issues, financial concerns, or health problems. While a certain level of anxiety is normal and can even be adaptive, excessive , chronic anxiety can interfere with daily functioning and may require professional treatment.
Fear and anxiety reduction procedures
Reducing fear and anxiety can involve various procedures, including:
Deep breathing exercises : Techniques like diaphragmatic breathing can help calm the nervous system.
Mindfulness and meditation: Practices that promote present-moment awareness can reduce anxiety levels.
Progressive muscle relaxation: Systematically tensing and relaxing muscles can alleviate physical tension associated with anxiety.
Cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT): Therapeutic approaches that challenge and reframe negative thought patterns .
Exposure therapy: Gradual exposure to feared situations or objects in a controlled setting to reduce anxiety over time.
Physical exercise : Regular activity can release endorphins, which improve mood and reduce anxiety.
Seeking support : Talking to friends, family, or a therapist can provide reassurance and coping strategies.
Limiting caffeine and alcohol intake : These substances can exacerbate anxiety symptoms.
Establishing a routine : Consistent daily schedules can provide a sense of stability and predictability.
Prioritizing self-care : Engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation, such as hobbies or spending time in nature.




