Deworming is a practice done to eliminate and prevent the spread of intestinal parasites, or worms, in the human body. Here are the reasons why you should consider deworming and how often it should be done:
Health Risks: Worms are parasites that live in the human intestines and depend on the host for nutrition and survival. They can cause a range of health problems, including poor nutrition, anemia (due to blood loss), stunted growth in children, and impaired cognitive development. By eliminating these parasites through deworming, you can reduce the risk of these health complications.
Prevalence: Intestinal worms are widespread in many parts of the world, particularly in regions with poor sanitation and hygiene practices. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), more than 2 billion people are affected by intestinal worms globally. Deworming is especially important in areas where soil-transmitted helminths (a type of intestinal worm) are common.
Recommended Frequency: Experts generally recommend deworming every six months, or twice a year, starting from the age of two. This regularity helps to break the life cycle of the worms and prevent reinfestation. However, the recommended frequency may vary depending on factors such as the prevalence of worms in your region, individual risk factors, and the advice of healthcare professionals.
Types of Worms:
There are different types of worms that can cause infections in humans. Some common examples include:
Tapeworms:
Tapeworms can be contracted by ingesting tapeworm eggs or larvae through contaminated water or undercooked meat. They can grow to a significant length inside the intestines and remain there for many years.
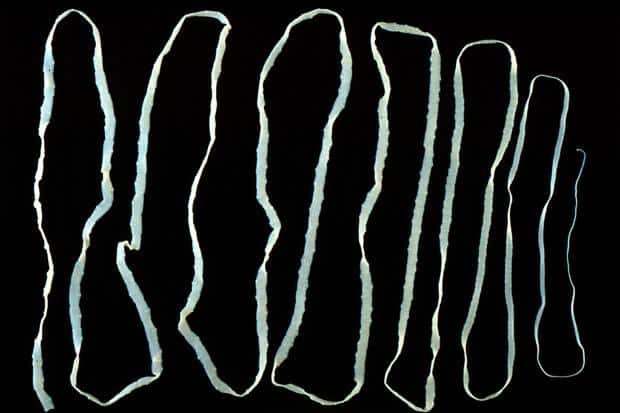
An adult tape worm, (4 metres long) removed from a gut
Hookworms:
Hookworms are roundworms that are transmitted through contact with contaminated soil. They can penetrate the skin, usually through barefoot contact, and migrate to the small intestine where they attach themselves to the intestinal wall.
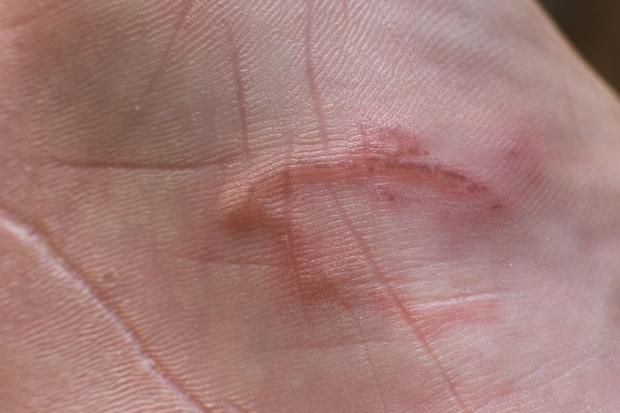
Rash on sole of foot, caused by the burrowing larvae of a hookworm
Trichinella:
Trichinella is a roundworm that is transmitted to humans by consuming undercooked meat containing larvae. This type of roundworm infection is known as trichinosis.
Symptoms of Worm Infestation:
Symptoms of worm infestation can vary but may include abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, gas and bloating, fatigue, unexplained weight loss, abdominal pain or tenderness, and the presence of worms in the stool. In some cases, a rash or itching around the rectum or vulva may occur.
Prevention:
Practicing proper hygiene is crucial in preventing the spread of worms. This includes washing hands thoroughly, especially before and after using the restroom, consuming clean water, consuming well-prepared food, and washing fruits, vegetables, and salads in clean water. Proper cooking of meat can also help prevent trichinosis.
It’s important to consult with healthcare professionals or follow local health guidelines regarding deworming practices specific to your region, as recommendations may vary based on the prevalence of worms and individual circumstances.




