
In the lush landscapes of Kenya, where biodiversity flourishes, beekeeping has been a traditional practice for centuries. However, in recent years, a modernization wave has swept through the beekeeping industry as the demand for honey continues to soar both domestically and internationally. With the allure of higher profits and increased efficiency, Kenyan bee farmers are increasingly turning towards modern beekeeping techniques and technologies to capitalize on this growing market.
Kenya’s favourable climate and diverse flora provide an ideal environment for beekeeping, supporting a wide variety of floral sources that yield high-quality honey. Traditionally, beekeeping in Kenya involved rudimentary methods, such as using log hives or traditional basket hives, often resulting in lower yields and limited quality control. However, with the surge in demand for honey, driven by both domestic consumption and export opportunities, bee farmers are recognizing the need to adopt modern practices to remain competitive in the market.

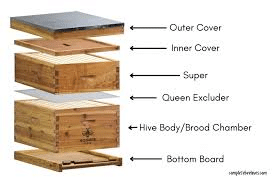
One of the key advancements in modern beekeeping is the use of modern beehives, such as Langstroth hives, which offer several advantages over traditional hives. Langstroth hives are designed to maximize honey production, ease of management, and bee health. These standardized hives allow for better hive inspection, pest control, and honey extraction, leading to higher yields and improved quality.
Moreover, technology is playing a significant role in revolutionizing beekeeping in Kenya. Bee farmers are increasingly embracing innovations such as hive monitoring systems, which utilize sensors to track hive conditions such as temperature, humidity, and hive weight remotely. These systems provide valuable insights into hive health and productivity, enabling beekeepers to make informed decisions and intervene promptly in case of any issues.
Furthermore, the adoption of modern beekeeping practices goes hand in hand with a focus on sustainable and eco-friendly methods. With increasing awareness of environmental conservation and the importance of pollinators in maintaining ecosystem balance, many bee farmers in Kenya are incorporating organic farming practices and avoiding the use of harmful chemicals in hive management. This not only ensures the production of high-quality honey but also contributes to the preservation of biodiversity and the health of the environment.

The shift towards modern beekeeping is also empowering local communities and driving socio-economic development in rural areas of Kenya. As beekeeping becomes more lucrative, it provides an alternative source of income for small-scale farmers, particularly in regions where traditional agriculture may be less profitable. Additionally, initiatives promoting beekeeping training and capacity-building are equipping farmers with the knowledge and skills needed to succeed in the modern beekeeping industry.
In response to the growing demand for honey, both domestically and internationally, Kenyan bee farmers are also exploring value-added products and diversifying their offerings. Beyond traditional honey production, beekeepers are venturing into producing beeswax, pollen, royal jelly, and other hive-derived products, catering to niche markets and increasing revenue streams.
The Government of Kenya, recognizing the potential of the beekeeping industry, has been supportive of initiatives aimed at modernizing the sector. Through policies promoting agricultural innovation, access to credit facilities, and market linkages, the government is facilitating the growth of modern beekeeping practices and encouraging entrepreneurship in the sector.
The rise of modern beekeeping in Kenya signals a promising future for the country’s beekeeping industry. By embracing innovation, technology, and sustainable practices, bee farmers are not only meeting the surging demand for honey but also contributing to economic development, environmental conservation, and community empowerment. As Kenya’s beekeeping sector continues to evolve, it holds the potential to become a beacon of success in the global apiculture market.





