Environmental pollution is one of the most pressing global issues today, affecting ecosystems, human health, and the planet’s climate. It refers to the introduction of harmful substances or products into the environment, causing adverse changes. Pollution is not a new phenomenon, but its scale and impact have increased dramatically with industrialization, urbanization, and the exponential growth of the global population. This article explores the causes, effects, and potential solutions to environmental pollution, highlighting the urgent need for collective action to mitigate its impact.

Causes of Environmental Pollution
1. Industrial Activities: Industrialization has significantly contributed to environmental pollution. Factories and power plants release large quantities of pollutants into the air, water, and soil. Common pollutants include sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, which are byproducts of burning fossil fuels. Industrial waste, often containing toxic chemicals, is frequently discharged into water bodies, contaminating drinking water and harming aquatic life.
2. Agricultural Practices: Modern agriculture, while essential for feeding the global population, is a major source of environmental pollution. The use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides leads to soil and water contamination. These chemicals can leach into groundwater, pollute rivers, and disrupt ecosystems. Additionally, the overuse of synthetic fertilizers contributes to air pollution through the release of nitrous oxide, a potent greenhouse gas.
3. Transportation: The transportation sector is a significant contributor to air pollution, primarily due to the combustion of fossil fuels in vehicles. Cars, trucks, airplanes, and ships emit carbon dioxide (CO2), carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). These emissions contribute to smog formation, respiratory problems, and global warming. The growing number of vehicles on the road, coupled with inefficient public transportation systems, exacerbates the problem.
4. Waste Management Issues: Improper waste disposal is a major cause of environmental pollution. Landfills, which are often not properly managed, can leak toxic substances into the soil and groundwater. The decomposition of organic waste in landfills also produces methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Additionally, the incineration of waste releases harmful pollutants into the air. Plastic waste, in particular, poses a severe threat to marine life and ecosystems, as it takes centuries to decompose and can cause entanglement or ingestion by animals.
5. Deforestation and Land Use Changes: The clearing of forests for agriculture, urban development, and logging leads to soil erosion, loss of biodiversity, and increased carbon emissions. Deforestation also disrupts the natural carbon cycle, contributing to climate change. Moreover, the destruction of natural habitats forces wildlife to migrate, often leading to human-wildlife conflicts and the spread of zoonotic diseases.
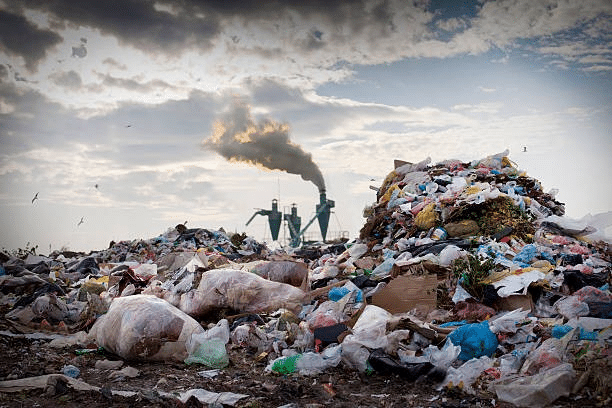
Effects of Environmental Pollution
1. Human Health Impacts: Environmental pollution has severe consequences for human health. Air pollution, for example, is linked to respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, and premature deaths. Polluted water sources can lead to waterborne diseases such as cholera and dysentery, particularly in developing countries with inadequate sanitation infrastructure. Long-term exposure to pollutants can also increase the risk of chronic illnesses, including cancer.
2.Ecosystem Damage: Pollution disrupts ecosystems by altering the natural balance of air, water, and soil. Airborne pollutants can damage vegetation, reduce crop yields, and acidify water bodies, harming aquatic life. Water pollution, caused by industrial discharge, agricultural runoff, and sewage, can lead to the death of fish, the destruction of coral reefs, and the disruption of food chains. Soil contamination affects plant growth, leading to a loss of biodiversity and the degradation of land.
3. Climate Change: Environmental pollution is a major driver of climate change. The release of greenhouse gases, such as CO2 and methane, from industrial activities, transportation, and deforestation contributes to global warming. Climate change leads to more frequent and severe weather events, rising sea levels, and shifts in ecosystems. The melting of polar ice caps, for example, is a direct consequence of increased global temperatures, threatening coastal communities and wildlife.
4. Economic Costs: The economic impact of environmental pollution is significant. The costs associated with healthcare, loss of productivity, and environmental cleanup are enormous. Pollution can also affect industries such as agriculture, tourism, and fisheries, leading to job losses and economic instability. Additionally, the degradation of natural resources reduces the availability of essential materials, impacting long-term economic growth and development.

Solutions to Environmental Pollution
1. Transition to Renewable Energy: One of the most effective ways to reduce environmental pollution is by transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydropower. These sources generate electricity without emitting harmful pollutants, significantly reducing air and water pollution. Governments and businesses must invest in renewable energy infrastructure and incentivize the adoption of clean technologies.
2. Sustainable Agricultural Practices: To reduce the environmental impact of agriculture, farmers can adopt sustainable practices such as organic farming, crop rotation, and the use of natural pest control methods. These practices minimize the use of harmful chemicals, reduce soil erosion, and protect water quality. Additionally, promoting plant-based diets can reduce the demand for resource-intensive livestock farming, further decreasing pollution.
3. Improved Waste Management: Proper waste management is crucial in reducing environmental pollution. Recycling, composting, and waste-to-energy technologies can significantly reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills and oceans. Governments should enforce strict regulations on waste disposal and encourage businesses and households to reduce, reuse, and recycle. Banning single-use plastics and promoting biodegradable alternatives are also essential steps.
4. Reforestation and Conservation: Reforestation and conservation efforts are vital in mitigating the effects of pollution and climate change. Planting trees helps sequester carbon dioxide, improve air quality, and restore degraded ecosystems. Protecting existing forests and biodiversity hotspots is equally important, as these areas act as natural buffers against pollution and climate change.
5. Public Awareness and Policy Action: Raising public awareness about the dangers of environmental pollution and the importance of sustainable practices is crucial for driving change. Governments must implement and enforce environmental regulations, set emission reduction targets, and promote green technologies. International cooperation is also necessary to address transboundary pollution and protect the global environment.
Environmental pollution is a complex and multifaceted problem that requires urgent attention and action. Its causes are deeply rooted in human activities, but with concerted efforts, it is possible to mitigate its impact. By transitioning to renewable energy, adopting sustainable practices, improving waste management, and protecting natural ecosystems, we can reduce pollution and safeguard the health of our planet for future generations. Collective action at the local, national, and global levels is essential in achieving a cleaner, healthier, and more sustainable world.




